记忆方法
1. an- "ana-, up" + od- "way" + -e.
2. => way up.
3. => So called from the path the electrical current was thought to take.
2. => way up.
3. => So called from the path the electrical current was thought to take.
中文词源
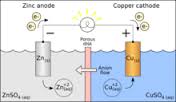
anode 阳极
前缀ana-, 向上。词根hod, 路,见odometer, 里程计,同词根ced, 走。
英语词源
- anode
-
anode: [19] The term anode, meaning ‘positive electrode’, appears to have been introduced by the English philosopher William Whewell around 1834. It was based on Greek ánodos ‘way up’, a compound noun formed from aná- ‘up’ and hodós ‘way’ (also represented in exodus ‘way out’ and odometer ‘instrument for measuring distance travelled’, and possibly related to Latin cēdere, source of English cede and a host of derived words). It specifically contrasts with cathode, which means literally ‘way down’.
=> exodus, odometer - anode (n.)
- 1834, coined from Greek anodos "way up," from ana "up" (see ana-) + hodos "way" (see cede). Proposed by the Rev. William Whewell (1794-1866), English polymath, and published by English chemist and physicist Michael Faraday (1791-1867). So called from the path the electrical current was thought to take. Related: Anodic.
权威例句
- 1. A red wire is often attached to the anode.
- 红色电线通常与阳极相联.
- 2. The reverse process may proceed at the anode.
- 相反的过程也会在阳极上发生.
- 3. The applied pressure acts on a diaphragm which in turn moves the anode pin.
- 施加的压力作用在一个膜片上,于是该膜片就移动阳极管脚.
- 4. It'shows well - defined wavelengths which are characteristic of the structure of the metal forming the anode.
- 它显示出那构成阳极的金属的结构所特有的,十分确定的波长.
- 5. The cathode rays are always beamed on a fresh area of the anode surface.
- 阴极射线总是射向阳极表面的新区域.